Have you ever considered why certain websites appear first in search results while others are tough to find? This difference can make or break businesses in a packed market. Search engines, specifically Google, help users find what they need online. When your site ranks below the top results, potential customers who purchase from you will remain unaware of your business’s existence.
Understanding how search engines operate is essential. These platforms apply complex algorithms that evaluate numerous factors to determine which sites earn top rankings. Keyword relevance, site speed, and user experience are crucial. If a business does not actively enhance its website for these elements, it risks outperforming rivals who are more aware of the requirements. Organisations that attempt to raise brand visibility without successful results remain unnoticed in an online space full of competitors.
Anyone can start these steps without prior tech knowledge. This blog will teach you about search engine operations to help improve your website. If you want more people to see your site, bring in more visitors, or boost sales, this guide has helpful tips to help you succeed online. By the end, you will have a straightforward plan to utilise search engines for your business growth.
What are Search engines?
Search engines are powerful software systems that help people find online information. They work like digital librarians putting in order and grouping billions of web pages to give valuable results for what users ask. To show how big this job is, Google handles more than 3.5 billion searches daily, about 40,000 searches every second. This vast operation demands significant computational power and advanced algorithms to ensure speed and accuracy.
The development of search engines illustrates significant technological progress. In the early Internet era, locating information was complex and required knowing precise website addresses or browsing directories. Beginning with Archie in 1990, which could only search file names, we have advanced to today’s search engines that comprehend context, user intent, and even natural language queries.
Significant developments in the history of search engines include:
- 1994: WebCrawler launched as the first full-text web crawler. It transformed how search engines indexed information, enabling users to search for any word on any webpage. This capability is now an essential part of web searching.
- 1998: Google introduced the PageRank algorithm. This innovation changed search results ranking, as it evaluated the number and quality of links to a page as indicators of its importance. This led to more relevant and accurate search results.
- 2009: Microsoft introduced Bing, which features enhanced visual search options and creates new market competition. Its integration with Microsoft products and emphasis on visual search offered users different search methods.
- 2015: Google launched RankBrain, a machine learning system designed to improve the processing and understanding of search queries. This represented a significant advancement towards AI-driven search technology.
- 2019: Implementing BERT-enhanced natural language comprehension, enabling search engines to grasp the context and subtleties of user queries more effectively.
- 2020s: Integrating AI and machine learning has transformed search engines into smart systems that understand natural language and user intent. Features like voice search and visual recognition have become more advanced and sophisticated.
The current search engine market has developed to include various types of search engines that serve distinct purposes:
- Specialised Search Engines: For example, job searching on Indeed or research about travel in Kayak.
- Academic Search Engines: Google Scholar and Microsoft Academic are services that specialise in providing intellectual publications and studies.
- Visual Search Engines: Pinterest and Google Lens offer applications that allow users to search with pictures instead of text.
- Privacy-Centric Search Engines: DuckDuckGo and Startpage let users search without saving their data.
Example: Google’s Evolution and Dominance
Google serves as an illustrative case for examining the development and influence of search engines.
- Early Development:
- In 1996, Larry Page and Sergey Brin launched their research project at Stanford University.
- When it first started in 1996, BackRub served as the name because the system centred on examining website backlinks.
- The company was formed in 1998 and worked with a 25 million web page database.
- Current Scale:
- Indexes more than 100 billion web pages.
- Dominates over 90% of the global search engine market.
- Supports searches in more than 150 languages.
- It uses over 200 factors to rank content in its algorithm.
- Innovation Timeline:
- 2001: Introduced Image Search
- 2004: Launched Local Search
- 2008: Added Google Suggest, now called Autocomplete
- 2011: Released Voice Search
- 2015: Began mobile-first indexing
- 2019: Rolled out BERT for natural language processing
- Other well-known search engines include:
- Bing: Microsoft runs 6% of all searches made worldwide.
- DuckDuckGo: It prioritises personal privacy and handles 100 million searches daily.
- Yahoo Search: Every month, the search engine handles 3 billion searches.
- Baidu: Baidu runs the leading search platform in China at 70%.
- Yandex: Yandex controls two-thirds of Russia’s search traffic.
How do Search Engines Work?
Search engines work through three main steps: crawling, indexing, and ranking. These processes have advanced over time to manage online content’s increasing complexity.
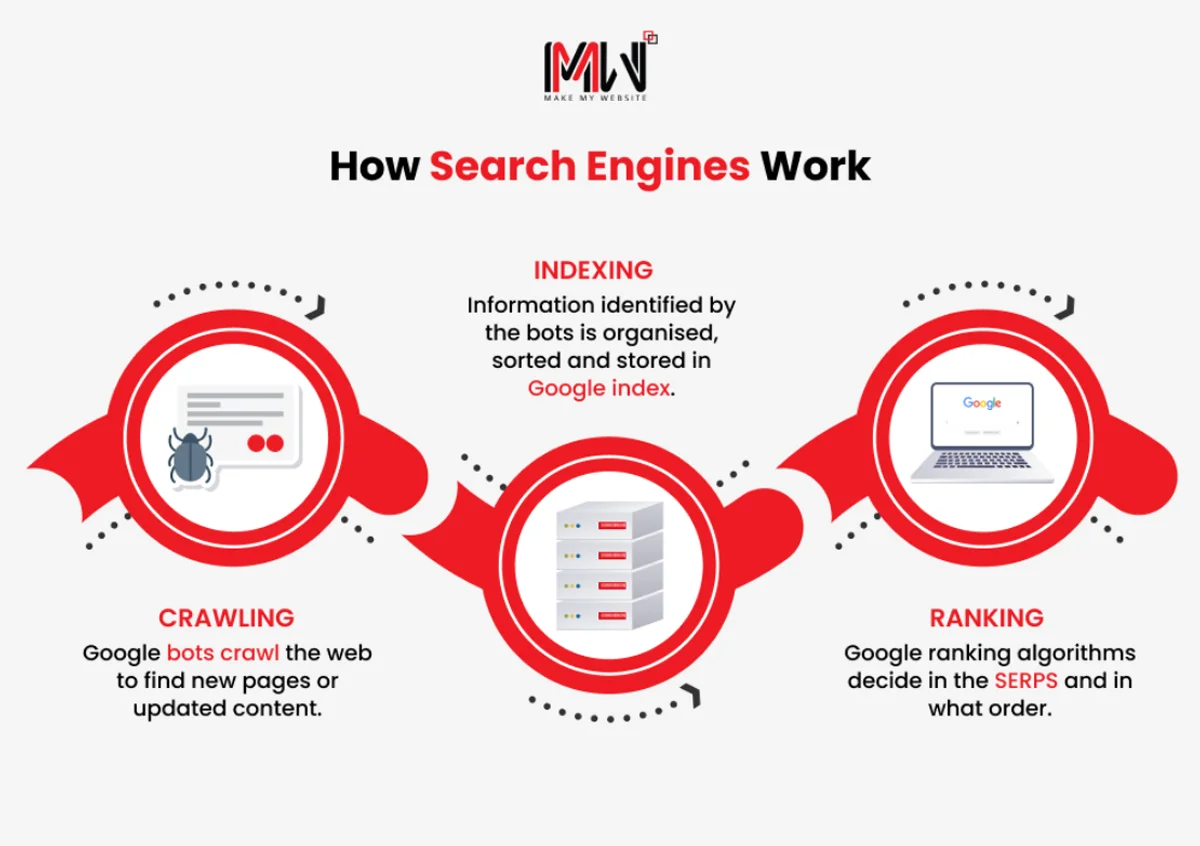
1. Crawling
Search engine crawlers, also called spiders, scan, and record website information. These tools follow links between pages to find new content and updates. Google’s crawler, Googlebot, processes billions of pages daily to keep its index current.
Modern crawling systems are highly advanced:
- Adaptive Crawling: Crawlers adjust how often they visit pages based on content updates. For example, news sites might be checked several times daily, while static pages are visited less often.
- Resource Management: Crawlers follow robots.txt guidelines and manage crawl rates to avoid overloading servers.
- JavaScript Handling: Today’s crawlers can process JavaScript and index content created dynamically, though it requires more resources.
- Mobile-First Crawling: With increased mobile usage, crawlers now prioritise viewing pages as they appear on mobile devices.
2. Indexing
The indexing process allows search engines to organise and store the gathered data. It involves sorting and categorising billions of pages to ensure fast access when required. Google’s index is believed to exceed 100 million gigabytes, spread across many data centres worldwide.
The indexing process consists of several detailed steps:
- Document Processing:
- Analysing HTML structure and parsing information
- Extracting and organising content into categories
- Detecting language and providing translation options
- Identifying and managing duplicate contentc
- Media Analysis:
- Recognising and categorising images
- Reviewing and interpreting video content
- Transcribing audio files
- Handling various file formats
- Metadata Collection:
- Understanding and processing schema markup
- Reviewing and interpreting meta tags
- Managing structured data
- Mapping link relationships
3. Ranking
Ranking is one of the most challenging parts of search engine operation. When a user types a search term, the system scans billions of indexed pages to find the most relevant options. Modern algorithms use hundreds of factors to decide the order of results.
Primary factors affecting rankings include:
- Content Factors:
- How well does the content match the search query
- Quality and thoroughness of the information
- Placement and use of targeted keywords
- Regular updates to keep content current
- Technical Factors:
- The speed at which the page loads
- Compatibility with mobile devices
- Use of HTTPS for secure browsing
- Performance-based on Core Web Vitals
- User Experience Factors:
- Rate of clicks from search results
- Time visitors spend on the page
- Percentage of users leaving quickly (bounce rate)
- Overall engagement from users
Related read: 3 Things To Include In a Website For Better Ranking
Components of Search Engine
A modern search engine consists of several advanced parts that deliver relevant results. Each part has an important role, from processing the query to showing the final results.
1. User Interface
The user interface is where users interact with a search engine. When Google launched its simple and clean interface in 1998, it changed how people used search engines. Today, this design handles over 2 trillion searches every year. Modern search interfaces include many features while focusing on simplicity and ease of use.
Primary interface features include:
- Search Options:
- Auto-complete provides suggestions based on common searches
- Voice search allows hands-free use
- Camera input enables searches using images
- Keyboard shortcuts improve efficiency for experienced users
- Search Results:
- Enhanced snippets include more visual details
- Knowledge panels offer quick facts
- Local results highlight location-specific queries
- News carousels present updates on current events
- Shopping features display products for easy browsing
2. Query Processor
The query processor interprets what users mean when they search. This advanced system converts natural language inputs into organised searches that the engine can interpret. Google research shows that 15% of daily searches are entirely new, highlighting the importance of having a strong query processing system.
The query processor performs several important tasks:
- Language Processing:
- Understanding natural language
- Correcting spelling and providing suggestions
- Expanding and refining queries
- Identifying and categorising user intent
- Contextual Analysis:
- Considering the user’s location
- Incorporating search history
- Optimising for specific devices
- Detecting languages and offering translations
3. Database Management System
The database management system is essential for search engines. It manages the storage and retrieval of indexed data, handling billions of queries while ensuring responses are delivered in under a second.
Modern search engine systems handle:
- Data Storage and Access:
- Store data across multiple global centres
- Process data immediately as it’s received
- Maintain backups and redundancy for safety
- Use caching for frequently searched queries
- Improving Performance:
- Balance server loads to handle the demand
- Use methods to speed up query processing
- Compress data to save space and improve speed
- Divide indexes into smaller parts for quicker searches
4. Business Applications
Search engines help businesses grow their market position successfully. Research demonstrates that customers begin their Internet searches on engines 68% of the time, thus making search engine optimisation vital for business development.
- Digital Marketing Applications:
- Improving organic reach through Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
- Running Pay-Per-Click (PPC) ad campaigns
- Planning and executing content marketing strategies
- Tracking brand mentions and managing online reputation
- Market Intelligence:
- Studying and monitoring competitors
- Spotting trends in the market
- Analysing consumer behaviours and preferences
- Researching and developing new products
Related read: How to Optimise Website For Search Engines
5. Educational Purpose
Search engines have reshaped education, with 94% of teachers stating their students use them for research tasks.
- Academic Uses:
- Finding and verifying research papers
- Gathering and reviewing literature
- Checking and confirming citations
- Opportunities for academic partnerships
- Access to Educational Materials:
- Locating online courses
- Creating teaching resources
- Organising learning materials for students
- Supporting remote education
6. Personal Use
People use search engines daily for various tasks, with most individuals performing 3-4 searches daily.
Typical personal uses include:
- Finding Information:
- Getting updates on news and events
- Checking weather and traffic details
- Looking up health or medical information
- Comparing product reviews
- Lifestyle and Entertainment:
- Discovering restaurants and venues
- Planning and booking trips
- Searching for recipes and cooking tips
- Accessing entertainment content
How do We Use a Search Engine?
Applying basic and advanced techniques for faster, more accurate results is essential to use search engines effectively.
1. Basic Search Techniques
Effective searching begins with creating well-thought-out queries. Instead of general terms, focus on precise, descriptive keywords that reflect the purpose of the search.
Key search techniques include:
- Query Creation:
- Use relevant and specific keywords
- Include necessary details like location, date, or type
- Avoid extra or irrelevant words
- Use natural language for more complex searches
- Evaluating Results:
- Assess the credibility of sources
- Compare findings across multiple results
- Confirm the accuracy of the information
- Check how recent the results are
2. Advanced Search Techniques
Experienced users can use advanced search tools and filters to narrow their search results effectively:
- Advanced Tools:
- Use “quotation marks” to find exact phrases
- Use the site to search within a specific domain
- Use filetype to locate certain document formats
- Use -exclude to filter out unwanted results
- Filtering Options:
- Limit results by date range
- Filter based on location
- Choose preferred languages
- Narrow results by type, such as images, news, or videos
3. Best Practices
To improve search effectiveness, users should stick to proven methods:
- Search Approach:
- Begin with general terms, then narrow them down
- Conduct multiple searches for complex subjects
- Use advanced filters when appropriate
- Save helpful searches for later use
- Privacy Guidelines:
- Use private browsing when required
- Understand how search history affects results
- Manage personal details carefully
- Consider alternative search engines for sensitive topics
Partner with Make My Website to Transform Your Online Presence
Understanding how search engines function is key to building a strong online presence. However, achieving higher rankings and staying ahead demands more than knowledge—skill, persistence, and the right resources. This is where Make My Website can assist.
Our team provides customised solutions for businesses aiming to excel online. We design user-friendly and visually attractive websites while applying effective SEO strategies. Our primary focus is to deliver valuable outcomes. Our team has what it takes to make your desired outcomes happen, whether you need better search engine placement, more website visitors, or loyal customers from your visitor pool.
Avoid letting the challenges of SEO stop your progress. With Make My Website by your side, you’ll have a committed team focused on making your business stand out online. We’ll simplify SEO, so your business can grow in today’s competitive market. Contact us today and take the first step towards online success



















